An isotonic solution (e.g., 0.9% sodium chloride) will have an osmolarity of approximately 280 mOsm/L, and cells placed in it will neither shrink nor swell. A cell placed in a hypotonic solution (< 280 mOsm/L) will swell, and those placed in a hypertonic solution (> 280 mOsm/L) will shrink.
Nuclear changes and actin filament organization in hASC after exposure… | Download Scientific Diagram
In this case, the cell swells, because urea penetrates the cell, raising the osmolarity and causing a net flow of water into the cell. This is because there is 600 mOsM urea in the solution and 500 mOsM NaCl in the RBC; the solution is 1000 mOsM total and the cell is 500 mOsM thus it is hyperosmotic.

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
The normal plasma osmolarity for solutions to be administered to large animals is approximately 306 mOsm/L; solutions can therefore be defined as isotonic (300-312 mOsm/L), hypertonic (>312 mOsm/L), or hypotonic (<300 mOsm/L).

Source Image: brainly.com
Download Image
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion: An overview Only if red blood cells are placed in isotonic solutions that have the same osmolarity as exists inside the cells are they unaffected by negative effects of osmotic pressure (Figure \(\PageIndex2b\)). Glucose solutions of about 0.31 M, or sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions of about 0.16 M, are isotonic with blood plasma.

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
Blood Cells Placed In A 500 Mosm/L Solution Will
Only if red blood cells are placed in isotonic solutions that have the same osmolarity as exists inside the cells are they unaffected by negative effects of osmotic pressure (Figure \(\PageIndex2b\)). Glucose solutions of about 0.31 M, or sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions of about 0.16 M, are isotonic with blood plasma. Oct 11, 2023A cell that does not have a rigid cell wall, such as a red blood cell, will swell and lyse (burst) when placed in a hypotonic solution. Cells with a cell wall will swell when placed in a hypotonic solution, but once the cell is turgid (firm), the tough cell wall prevents any more water from entering the cell. When placed in a hypertonic
Red blood cells under the microscope, hypo and hypertonic solutions – YouTube
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like If red blood cells are placed in a 300 mOSM solution of a solute there will be no net movement of water across the plasma membrane. -true under all circumstances -only true if the solute is a penetrating solute -true only if the solute is detergent Dextrose in Lactated Ringer’s: Package Insert – Drugs.com

Source Image: drugs.com
Download Image
Fluid selection using pH-guided resuscitation Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like If red blood cells are placed in a 300 mOSM solution of a solute there will be no net movement of water across the plasma membrane. -true under all circumstances -only true if the solute is a penetrating solute -true only if the solute is detergent
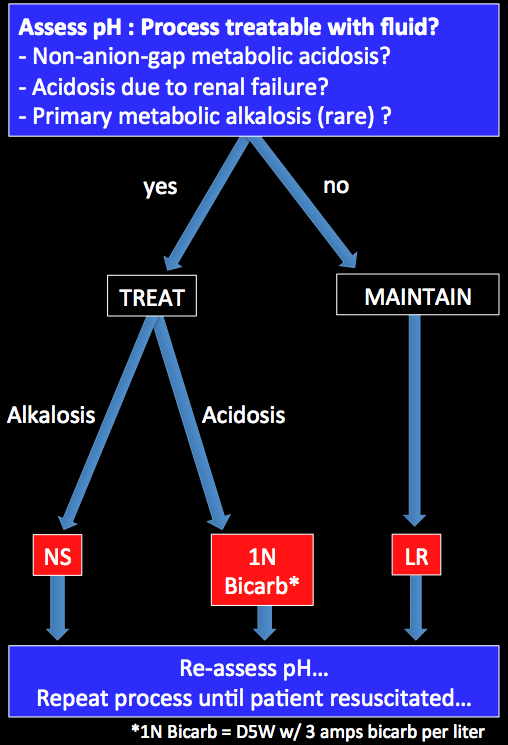
Source Image: emcrit.org
Download Image
Nuclear changes and actin filament organization in hASC after exposure… | Download Scientific Diagram An isotonic solution (e.g., 0.9% sodium chloride) will have an osmolarity of approximately 280 mOsm/L, and cells placed in it will neither shrink nor swell. A cell placed in a hypotonic solution (< 280 mOsm/L) will swell, and those placed in a hypertonic solution (> 280 mOsm/L) will shrink.

Source Image: researchgate.net
Download Image
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion: An overview The normal plasma osmolarity for solutions to be administered to large animals is approximately 306 mOsm/L; solutions can therefore be defined as isotonic (300-312 mOsm/L), hypertonic (>312 mOsm/L), or hypotonic (<300 mOsm/L).

Source Image: medicalnewstoday.com
Download Image
Session 5 Flashcards by Georgina Yan | Brainscape In general, hemolysis occurs at extracellular concentrations less than 180 mOsm and crenation occurs at extracellular concentrations greater than 500 mOsm. Review of osmolarity OSMOLARITY is the concentration of molecules in a solution that can influence the movement of water.

Source Image: brainscape.com
Download Image
Is post-hypertonic lysis of human red blood cells caused by excessive cell volume regulation? – ScienceDirect Only if red blood cells are placed in isotonic solutions that have the same osmolarity as exists inside the cells are they unaffected by negative effects of osmotic pressure (Figure \(\PageIndex2b\)). Glucose solutions of about 0.31 M, or sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions of about 0.16 M, are isotonic with blood plasma.

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Normal Lab Values: Complete Reference Cheat Sheet (2023) – Nurseslabs Oct 11, 2023A cell that does not have a rigid cell wall, such as a red blood cell, will swell and lyse (burst) when placed in a hypotonic solution. Cells with a cell wall will swell when placed in a hypotonic solution, but once the cell is turgid (firm), the tough cell wall prevents any more water from entering the cell. When placed in a hypertonic
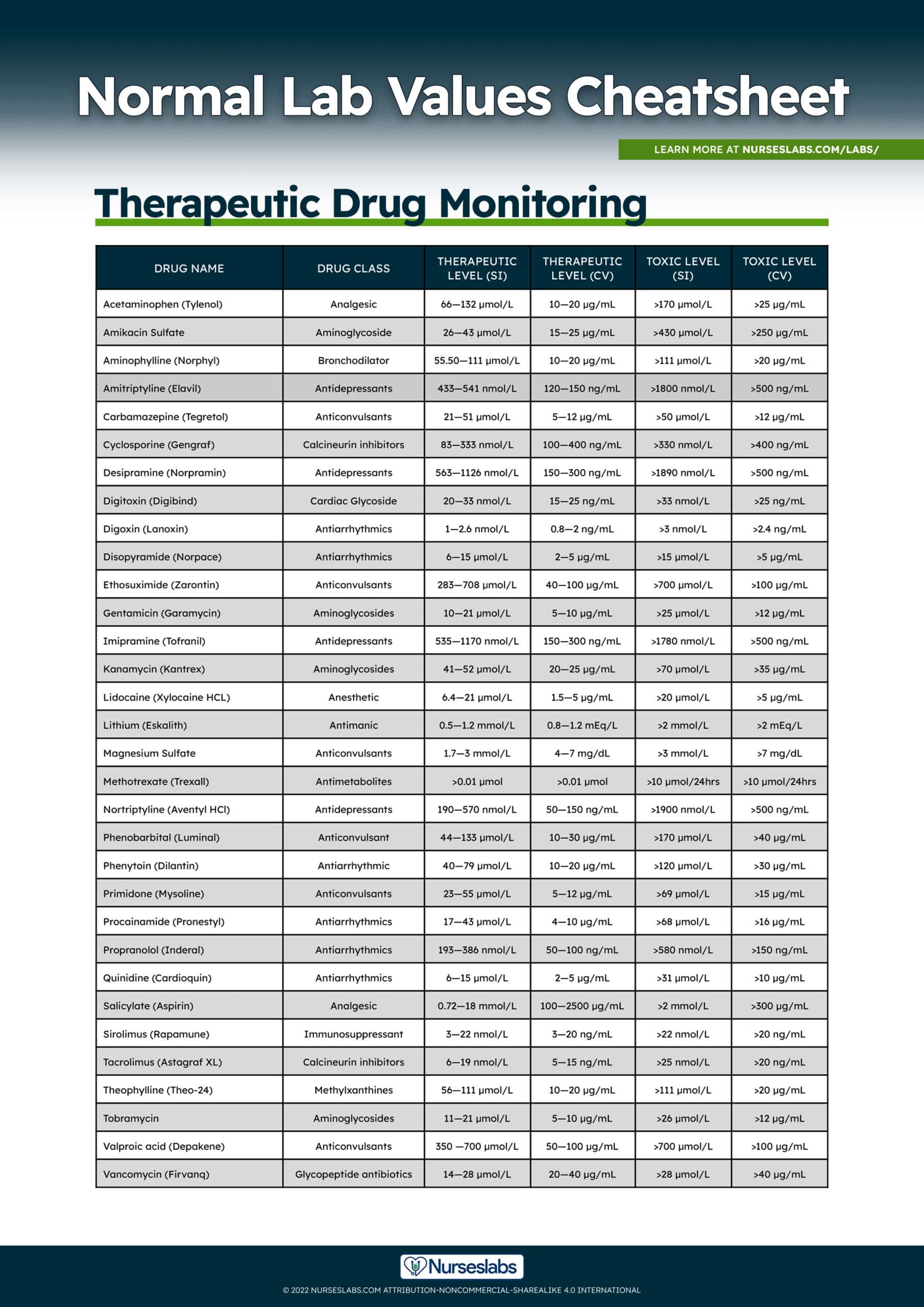
Source Image: nurseslabs.com
Download Image
Fluid selection using pH-guided resuscitation
Normal Lab Values: Complete Reference Cheat Sheet (2023) – Nurseslabs In this case, the cell swells, because urea penetrates the cell, raising the osmolarity and causing a net flow of water into the cell. This is because there is 600 mOsM urea in the solution and 500 mOsM NaCl in the RBC; the solution is 1000 mOsM total and the cell is 500 mOsM thus it is hyperosmotic.
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion: An overview Is post-hypertonic lysis of human red blood cells caused by excessive cell volume regulation? – ScienceDirect In general, hemolysis occurs at extracellular concentrations less than 180 mOsm and crenation occurs at extracellular concentrations greater than 500 mOsm. Review of osmolarity OSMOLARITY is the concentration of molecules in a solution that can influence the movement of water.